In the ever-evolving world of materials, one substance stands out for its exceptional strength, transparency, and versatility – polycarbonate. This remarkable thermoplastic polymer has revolutionized numerous industries, captivating professionals, hobbyists, and consumers alike with its unique properties. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast, a manufacturer, or simply curious about cutting-edge materials, this comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating realm of polycarbonate.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer renowned for its exceptional strength and durability. Its chemical composition consists of repeating units of bisphenol A and phosgene, giving it a unique molecular structure that contributes to its remarkable properties. Classified as a naturally transparent amorphous thermoplastic, polycarbonate can internally transmit light almost as effectively as glass, withstand impacts, and be moulded and reformed without cracking or breaking, making it highly versatile for various applications.
Properties of Polycarbonate
Transparency and Clarity
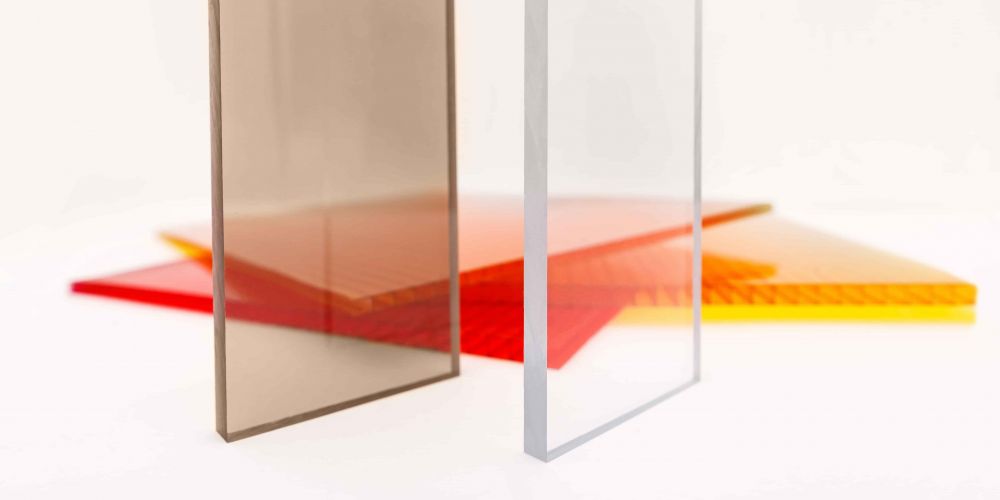
One of the standout features of polycarbonate is its exceptional transparency and clarity, making it an ideal choice for applications where visibility is essential, such as glazing, lenses, and protective enclosures. Polycarbonate can transmit up to 88% of visible light, providing excellent optical clarity.
Polycarbonate lenses are widely used in various applications such as eyewear and protective gear.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polycarbonate is virtually unbreakable and can withstand significant impacts without shattering. Its impact resistance is a staggering 200 times greater than glass, making it an exceptional choice for safety applications. This material can withstand repeated impacts of over 900 joules of energy without cracking or breaking. However, polycarbonate has low scratch resistance, so a hard coating is often applied to improve its durability, especially in applications like eyewear lenses and automotive headlamp lenses.
Heat Resistance and Workability
This versatile material can withstand high temperatures without deforming, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including those involving heat exposure. Polycarbonate retains its strength and stability at temperatures up to 115°C, well above the melting point of many other thermoplastics. Its excellent heat deflection temperature (HDT) of around 132°C ensures it maintains dimensional stability in high-temperature environments. Additionally, polycarbonate exhibits strong chemical resistance, making it compatible with various substances and enhancing its durability in different applications.
Electrical and Optical Properties
Polycarbonate exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties making it widely used in electrical and electronic applications. It also boasts superior optical properties allowing it to be used for high-quality lenses, eyewear, and specialised optical components with minimal distortion.
Polycarbonate plastic is also commonly used in electronic devices and other consumer products due to its UV resistance, transparency, and stability at higher temperatures.
Advantages of Polycarbonate
Lightweight yet Strong
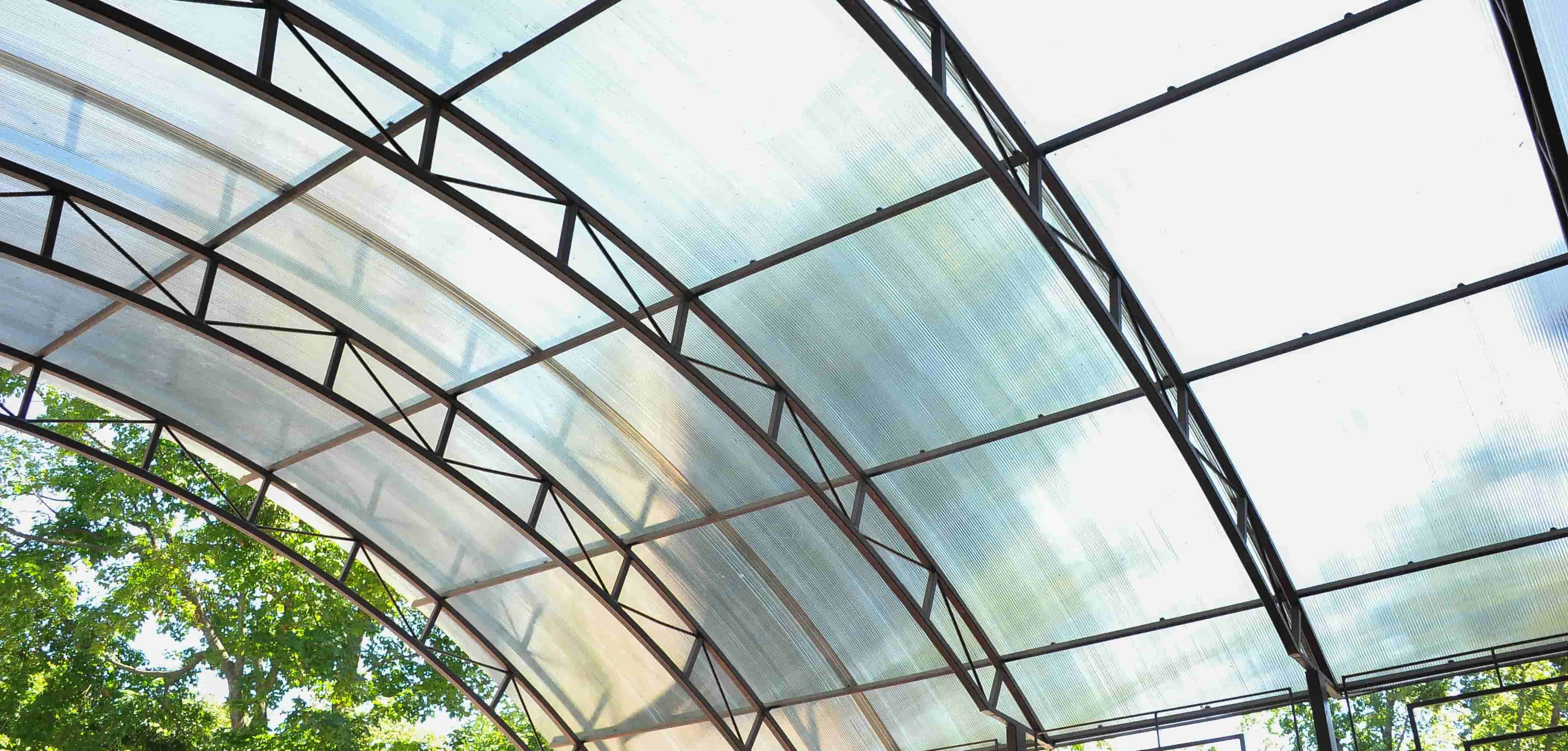
Despite its remarkable strength, polycarbonate is lightweight, with a density of approximately 1.2 g/cm³, making it easy to handle and install, reducing strain and fatigue in various applications. It offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, enabling the creation of durable yet lightweight products and structures. Polycarbonate sheeting is commonly used in applications such as roofing and glazing due to its UV protection, weather resistance, and versatility in various sizes, shapes, colours, and transparencies.
Shatter-Resistant and Virtually Unbreakable
Polycarbonate’s shatter-resistant nature is a game-changer for many industries. Its exceptional tensile strength, which measures its resistance to breaking under tension or stretching forces, and flexural strength, which indicates its ability to withstand bending or flexing, make it virtually unbreakable. Even under extreme stress conditions that would cause other materials to crack or shatter, polycarbonate remains intact and long-lasting, thanks to its remarkable durability. However, the use of polycarbonate containers for food storage is controversial due to concerns over the release of bisphenol A (BPA), especially at high temperatures.
Excellent Insulation Properties
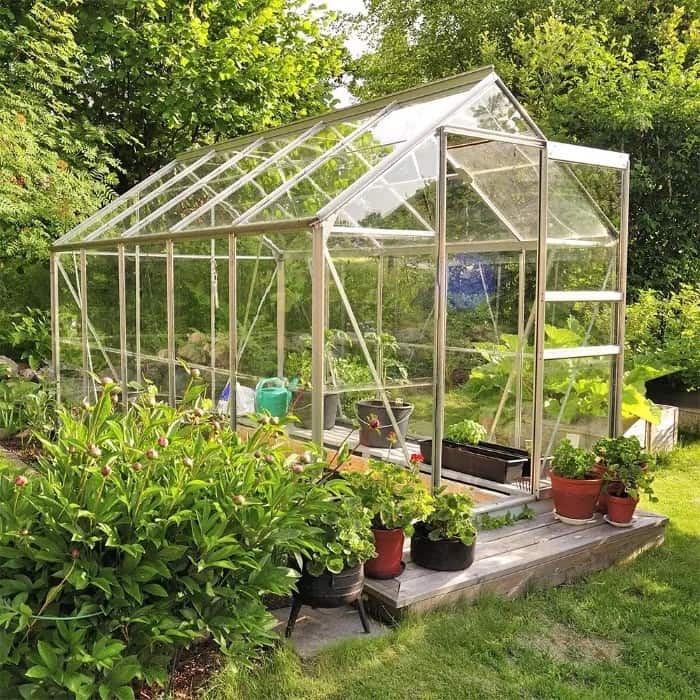
Polycarbonate excels as an insulator, with a low thermal conductivity that effectively prevents heat transfer. This makes it ideal for applications like greenhouses and insulated structures, helping maintain desired temperatures and reduce energy costs. Additionally, its sound insulation properties mitigate noise pollution.
Furthermore, polycarbonate's enhanced UV resistance slows down erosion caused by natural light, extending the service life of products and providing protection on both sides of the sheet.
Versatile and Easy to Fabricate
Polycarbonate's versatility allows for easy cutting, drilling, sawing, and machining using standard tools. It can be cold-formed, thermoformed, or bent into complex shapes without compromising strength or optical properties. Polycarbonate is also compatible with various joining methods, enabling flexible assembly and construction processes, making it an attractive choice for DIYers, manufacturers, and designers.
Applications of Polycarbonate Sheets